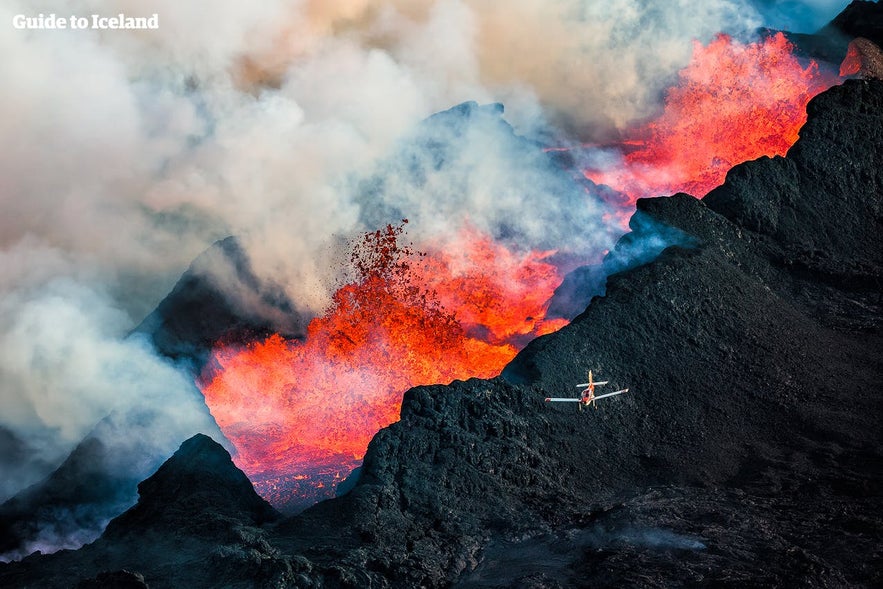
Holuhraun is an immense lava field north of Vatnajökull glacier in Iceland's Highlands. The most recent major eruption in Iceland occured here, beginning on 29 August 2014 and ending on 27 February 2015.
This eruption created a vast lava field of more than 85 km² (33 mi²), the largest to be produced in the country since the year 1783.
当サイトの情報が信頼できる理由
Guide to Iceland (ガイド・トゥ・アイスランド)は、アイスランドで最も信頼されている旅行プラットフォームです。毎年、何百万人もの旅行者にご利用いただいています。 すべてのコンテンツは、アイスランドに精通した現地の専門家が執筆・監修しており、 常に正確で最新の情報を提供しています。 信頼できる旅のアドバイスをお探しなら、ぜひ当サイトをご活用ください。
Recent Eruptions at Holuhraun
Holuhraun is in a highly volcanic area, sitting above both the Barðarbunga and Askja volcano systems. As such, it is composed of many layers of lava, which have been added to over centuries. Because Barðarbunga is beneath Vatnajökull glacier, the area has also washed over many times by glacial floods.
The lava that covered the area before 2014 was from a 1797 eruption of Askja. It was named Kvislahraun originally, before taking its current name in 1884.
The 2014 eruption started out when a vein of lava from the Barðarbunga volcano system because to push its way northward. Initially, it was feared this lava may occur beneath the glacier, which would cause ash clouds like seen in the 2010 eruption of Eyjafjallajökull, but it continued to move, seemingly trying to connect with the Askja system in a way unseen before.

It broke the surface of Holuhraun before it could reach it, however. Starting off with a small eruption on the northern side, the whole area was quickly engulfed in a sea of lava flowing from multiple fissures.
Within three months, the amount of lava that had been released was greater than any since the 1783 Laki eruption, which wiped out a quarter of the population, forced a quarter to flee, and created an ash cloud that plunged Europe, North Africa and the Middle East into famine and arguably France into revolution.
The eruption ended at the end of February in 2015, leaving Holuhraun much vaster than it was before.
No human deaths have been attributed to this eruption, but many sheep died due to poisons in the soil over the next year. The toxic gases also caused respiratory problems for those susceptible across the country whenever the wind blew in their direction, and on several days, residents of different towns were told to stay indoors unless absolutely necessary.
Holuhraun, however, was not considered a particularly dangerous eruption due to the fact that there are no settlements anywhere near it.
Surroundings of Holuhraun
As mentioned, Holuhraun is near to two large volcano systems; Askja’s crater is 15 kilometres (9 miles) to the north and Barðarbunga’s is 41 kilometres (26 miles) to the southwest. Directly to its south is the nearest glacier, Dyngjujökull, part of the greater Vatnajökull.
The glacial river of Jökulsá á Fjöllum is fed largely by the water that runs to the east of Holuhraun. This river holds the most powerful waterfall in Europe within it, Dettifoss.
Due to the remoteness of Holuhraun, and its distance from the major highland roads, it is difficult to reach. There is, however, an unnamed gravel road that leads from the route F910.