Hvalfjordur is a fjord in West Iceland. The fjord is approximately 30 kilometers (19 miles) long and five (three miles) kilometers wide and is home to the Hvammsvik Hot Springs spa and Glymur waterfall.
Hvalfjordur is a fjord in the west of Iceland and is about 19 miles (30 kilometers) long and 3.1 miles (5 kilometers) wide. Hvalfjordur fjord combines serene, untouched nature with historical significance, making it a less touristy yet highly attractive destination for hikers, nature lovers, and photographers. The fjord’s landscape includes small lakes, rivers, waterfalls, and picturesque mountains.
Why You Can Trust Our Content
Guide to Iceland is the most trusted travel platform in Iceland, helping millions of visitors each year. All our content is written and reviewed by local experts who are deeply familiar with Iceland. You can count on us for accurate, up-to-date, and trustworthy travel advice.
Despite its name, which translates to "Whale Fjord," Hvalfjordur fjord is not known for its whale population. However, it offers a rich bird life and is home to harbor seals. Two theories exist about how the fjord got its name: either that the fjord was once home to whales before fish stocks moved away, or the name could stem from the bay’s distinctive shape.
Natural attractions in the area are plentiful, but the most significant is Iceland's second-highest waterfall, Glymur, which runs from the Botnsa river. The area also has plenty of interesting hiking trails, such as the Sildarmannagotur path, leading north, and Leggjabrjotur trail, leading east towards Thingvellir National Park. It's an excellent area for hiking tours, and dor an extensive insight into the best trails, check out the complete guide to the best hikes and trails in Iceland!
Top Things To Do in Hvalfjordur Fjord
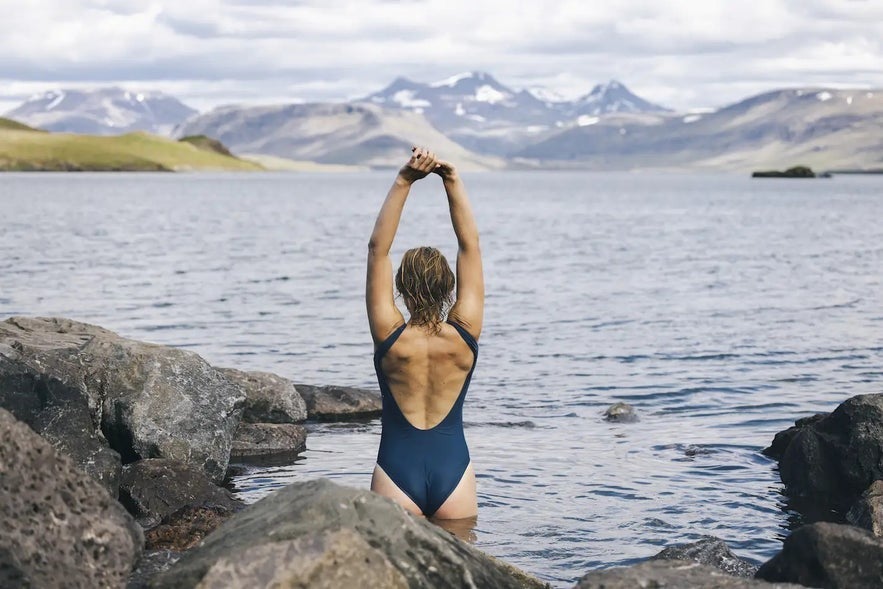

Bathe in Hvammsvik Hot Springs
Bathing in the geothermal hot springs of Iceland is, without a doubt, one of the must-try experiences when visiting. Hvammsvik Hot Springs in Hvalfjordur fjord includes eight pools with breathtaking views of the fjord and the surrounding landscape and opportunities to try paddleboarding, yoga, fishing, golf, cycling, farm tours, and even a Wim Hof Method session for those who dare. On clear winter nights, the resort can be an ideal place for unobstructed views of the northern lights when the activity is high.
What separates the Hvammsvik Hot Springs from the rest is that its water is a blend of underground water and seawater, which changes with the tides and seasons- giving a unique experience each time. In this resort, you will also find Stormur Bistro, a restaurant that offers hearty, light meals made with locally sourced ingredients. We highly recommend the bistro’s seafood soup, which has become one of its most popular dishes.
For the unique experience of bathing in the geothermal Hvammsvik Hot Springs while getting lost in the incredible view, you can book your admission here. You can also book an entry to Hvammsvik Hot Springs, which includes transportation from Reykjavik city center.
Hike To Glymur Waterfall
 One of the most notable attractions in Hvalfjordur fjord is Glymur, Iceland's second tallest waterfall, dropping from a height of 650 feet (198 meters). The hike to Glymur waterfall offers scenic views of the canyon, caves, cross rivers, and, of course, a panoramic view of the waterfall. The hike to Glymur waterfall is approximately 4.3 miles (7 kilometers) from the parking lot, and its difficulty is moderate.
One of the most notable attractions in Hvalfjordur fjord is Glymur, Iceland's second tallest waterfall, dropping from a height of 650 feet (198 meters). The hike to Glymur waterfall offers scenic views of the canyon, caves, cross rivers, and, of course, a panoramic view of the waterfall. The hike to Glymur waterfall is approximately 4.3 miles (7 kilometers) from the parking lot, and its difficulty is moderate.
To get the most out of this unique experience, you can go on a private guided hike to Glymur waterfall. Keep in mind that during the winter months, the hike can be very dangerous and near impossible, given unpredictable weather, uneven trails, and slippery paths.
Go Northern Lights Hunting in Hvalfjordur Fjord
Hvalfjordur fjord is an ideal place for northern lights hunting between late September and early April. Being away from the city lights and pollution gives you a unique chance to see this beautiful natural phenomenon with your bare eyes.
You can hunt for them yourself with a rental car by following the Iceland aurora forecast, or you can choose to book convenient northern lights tours to find the best spots with an expert guide.
How To Get To Hvalfjordur Fjord
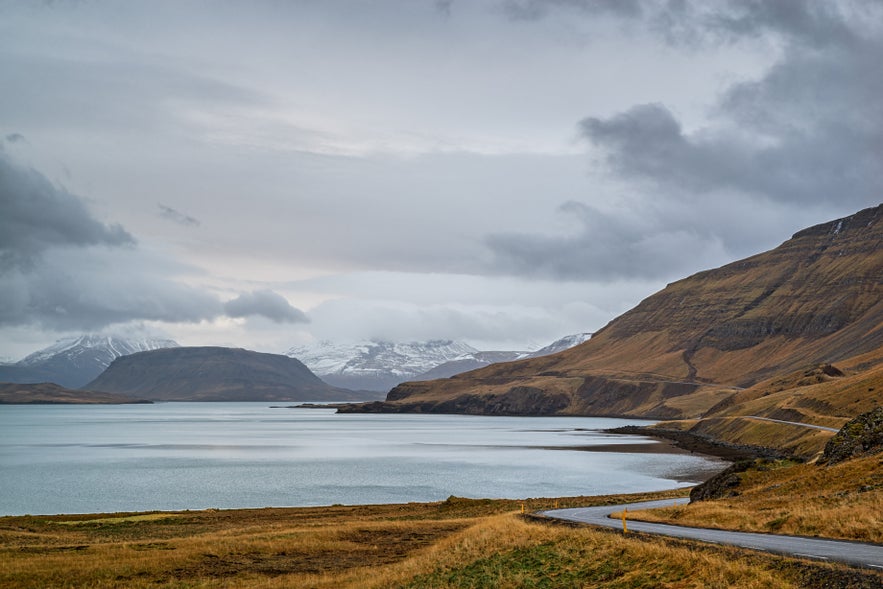

Hvalfjordur Tunnel
In the past, traveling around Hvalfjordur fjord required a rather lengthy drive of approximately 38.5 miles (62 kilometers). However, the opening of the Hvalfjordur tunnel in 1998 made the trip much shorter. The Hvalfjordur tunnel is about 3.59 miles (5.77 kilometers) long and runs beneath the fjord, significantly reducing travel time and making the region more accessible to locals and tourists alike. There is no fee to drive through the Hvalfjordur tunnel.
History and Culture of Hvalfjordur Fjord

Photo above from Wikimedia, Creative Commons, by Axel Kristinsson. No edits made.
World War II Legacy
During World War II, the British and American navies built bases along Hvalfjordur fjord for their naval operations due to its strategic location for protecting Atlantic convoys. Remains of this era can still be seen today, including piers and other infrastructure.
The Whaling Station in Hvalfjordur Fjord
Hvalfjordur fjord is home to the first Icelandic-owned whaling station, built in 1948 on Midsandur. The station is still in use today and stands as a reminder of the country's history of whaling as a part of its maritime culture, though highly controversial.
Notable Inhabitants of Hvalfjordur Fjord
Iceland's most prominent psalm poet, Hallgrímur Pétursson, lived in Hvalfjordur fjord. The area was also the home of the late Sveinbjörn Beinteinsson, poet and performer, and head of the Icelandic Pagan Association.
Grundartangi Industrial Site
Grundartangi Industrial Site in Hvalfjordur fjord includes one of the largest harbors in the country and two industrial plants. One is a ferrosilicon plant, which has been operating since 1979, and the other is an aluminum smelter, which has been operating since 1998. Both were controversial during construction and continue to be controversial during operation. Along with whaling and hydroelectric dams, smelters and silicon plants are the hottest environmental debates in Iceland.