Commissioned by Guide to Iceland and conducted by Gallup Iceland, the study was fielded between December 2025 and January 2026. A total of 427 tourism professionals across the sector responded, drawing on their regular interactions with international travelers.
The results summarize which nationalities tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently associate with key aspects of daily interaction, including communication, preparedness for Icelandic conditions, service-related challenges, and compliance with safety and environmental guidelines.
Cite this research
Copy-and-paste attribution:
Please link to this URL when referencing the findings or using the charts.
Key Findings
-
Ease of communication differs between nationalities. Tourism professionals most often associate travelers from the US, the UK, and Canada with smooth communication, while travelers from China, France, and Italy are linked with more communication challenges.
-
Preparation levels vary significantly. Travelers from Germany stand out as the best prepared for Iceland’s conditions, followed by Canada and the United States, while lower preparation is reported more often for some southern European and long-haul markets.
-
Service-related challenges follow similar patterns. Groups that are harder to communicate with are more frequently associated with service challenges, including delays, complaints, and mismatched expectations in day-to-day service interactions.
-
Compliance with safety and environmental guidelines is uneven. German, American, and British travelers are most often associated with strong compliance, while travelers from China and parts of southern Europe more frequently require additional guidance.
-
The findings point to practical improvements. Clearer communication, stronger expectation-setting, and more accessible information in more languages can reduce friction and improve safety for both travelers and tourism professionals.
Background

These challenges tend to surface most clearly in situations where local safety rules are shaped by conditions that may not be intuitive to visitors. Clear examples of this include the sneaker waves at Reynisfjara Black Sand Beach, the variable stability of glacial ice caves, and unfamiliarity with Iceland’s roads, which are governed by strict rules on where stopping is permitted. In all of these settings, seemingly minor decisions can carry elevated risk.
The purpose of this survey is to examine how tourism professionals in Iceland experience these recurring situations in practice, focusing on communication, preparedness, service-related challenges, and adherence to safety and environmental guidance between nationalities.
By identifying patterns reported across these factors, the study is intended to support more effective information, expectation-setting, and guidance for travelers and the industry alike.
Study Method

-
Respondents: The survey was distributed to tourism professionals working across the tourism sector, including the operators of accommodations, tours, and car rentals. All respondents interact regularly with international travelers.
-
Data collection method: Internet survey and phone calls.
-
Survey design: The survey consisted of six questions focusing on recurring situations related to communication, preparedness for Icelandic conditions, service-related challenges, and adherence to safety and environmental guidelines.
-
Response format: For each question, respondents selected their top three nationalities from a list of the ten largest travel nationalities in Iceland (the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Spain, France, Italy, and China), with an additional “other” option.
-
Response rate: The survey was sent to 1,773 individuals, of whom 427 responded, resulting in a response rate of 24.1%, which is considered strong for voluntary industry surveys in the Nordic region.
The Six Survey Questions and Their Results
The survey questions look at key parts of daily interaction between tourism professionals and international travelers in Iceland. For each question, respondents identified the nationalities they most often associate with each of these areas of interaction.
The six questions of the survey:
-
From which country or countries are tourists the easiest to communicate with?
-
From which country or countries are tourists the most difficult to communicate with?
-
From which country or countries do tourists most often create challenges in service?
-
From which country or countries are tourists most likely to comply with Icelandic safety and environmental guidelines?
-
From which country or countries are tourists most likely to disregard Icelandic safety and environmental guidelines?
-
From which country or countries are tourists best prepared for traveling in Iceland?
The brief commentary accompanying the results for each question below offers contextual interpretation based on industry knowledge and experience, and should not be read as conclusions drawn directly from the survey data.
Full Results Table by Country
| Country | Easiest communication | Most difficult communication | Service challenges | Comply with guidelines | Disregard guidelines | Arrive prepared | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total % | Index | Total % | Index | Total % | Index | Total % | Index | Total % | Index | Total % | Index | |
| US | 73.8% | 65.3 | 11.0% | 8.2 | 29.1% | 23.7 | 36.7% | 29.9 | 23.2% | 18.1 | 29.3% | 22.9 |
| UK | 55.5% | 38.3 | 3.3% | 2.2 | 3.4% | 2.3 | 32.9% | 23.5 | 6.8% | 4.3 | 24.4% | 15.0 |
| Canada | 40.3% | 22.5 | 0.3% | 0.2 | 0.6% | 0.4 | 30.1% | 17.1 | 0.6% | 0.4 | 38.4% | 25.3 |
| Germany | 31.8% | 20.8 | 9.8% | 6.8 | 14.9% | 10.4 | 68.7% | 58.9 | 4.5% | 3.4 | 75.9% | 66.3 |
| Netherlands | 19.1% | 11.0 | 4.8% | 3.1 | 4.0% | 2.7 | 28.2% | 16.4 | 1.3% | 1.0 | 27.1% | 14.3 |
| Poland | 8.3% | 4.5 | 2.1% | 1.0 | 1.5% | 0.8 | 5.3% | 3.1 | 7.4% | 4.4 | 10.4% | 5.6 |
| Spain | 6.4% | 3.4 | 14.0% | 7.5 | 11.1% | 7.5 | 2.5% | 1.6 | 15.2% | 7.7 | 4.3% | 2.1 |
| France | 4.1% | 2.9 | 33.9% | 24.5 | 26.9% | 18.6 | 10.3% | 5.4 | 14.8% | 9.6 | 15.5% | 9.8 |
| Italy | 4.4% | 2.6 | 21.1% | 11.4 | 15.5% | 9.7 | 2.2% | 1.3 | 17.4% | 10.0 | 8.8% | 4.6 |
| China | 3.6% | 2.5 | 67.3% | 58.6 | 46.1% | 38.9 | 4.7% | 3.8 | 80.3% | 74.8 | 4.3% | 3.7 |
| Other | 10.5% | 6.4 | 42.3% | 35.2 | 46.4% | 39.5 | 8.2% | 6.5 | 25.8% | 18.9 | 5.8% | 4.4 |
The percentages shown reflect the share of respondents who selected each nationality among their top three choices for a given question. Because respondents could select more than one nationality per question, percentages do not total 100%.
The index score reflects the strength of association between each nationality and a given category, based on a weighted ranking of first, second, and third mentions. First mentions carry the greatest weight, followed by second and third mentions. A higher index indicates a stronger relative association within that category.
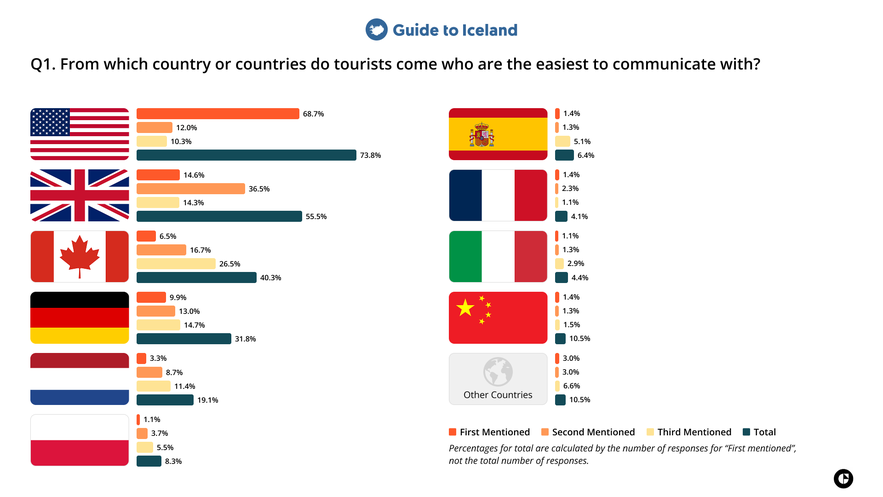
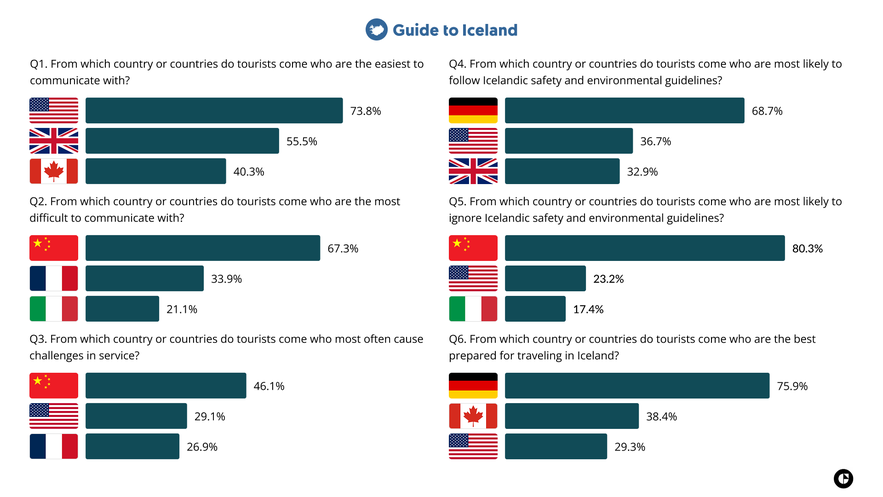
1. From which country or countries are tourists the easiest to communicate with?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently identified travelers from the United States as the easiest to communicate with. Visitors from the United Kingdom and Canada were also commonly mentioned in this category. Among non-English-speaking countries, Germany and the Netherlands were most often associated with smooth communication.
Commentary
Clear communication tends to be easiest when travelers and tourism staff share a common working language and similar expectations around service interactions. English-speaking travelers may find it easier to understand safety briefings, directions, and service information, while tourism staff are naturally accustomed to communicating in English.
While a shared language cannot be identified as a definitive explanation, the next highest-ranking nationalities are non-native English speakers known for strong English proficiency and international travel experience, pointing to communication ease beyond native language alone.
Tourism professionals tend to experience interactions more positively when travelers can easily understand briefings, ask questions, and follow updates as they arise.
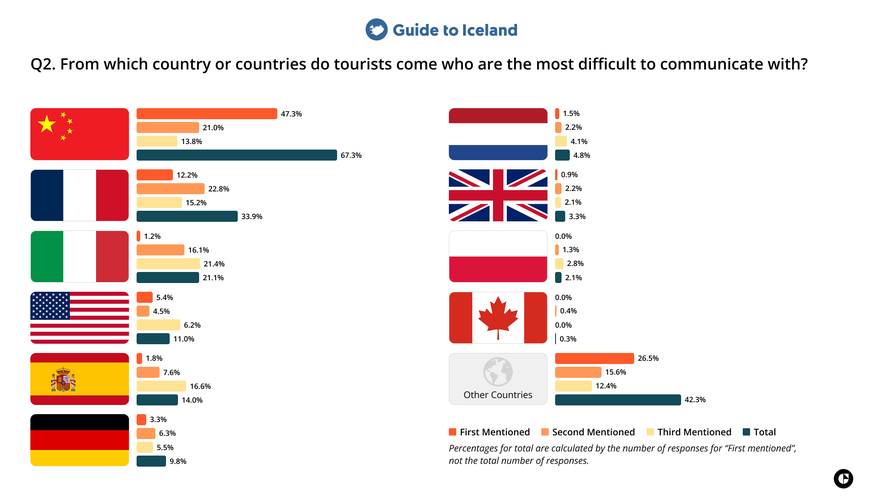
2. From which country or countries are tourists the most difficult to communicate with?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently identified travelers from China as the most difficult to communicate with. Visitors from France and Italy were also commonly mentioned in this category. In addition, a substantial share of respondents selected “Other countries,” meaning the nationalities they most associate with communication difficulties were not among the ten largest source markets listed in the survey.
Commentary
Communication challenges can arise for many reasons, and access to information in a language travelers fully understand is one of them. When pre-arrival materials, signage, or on-site guidance are not available in a familiar language, messages are more easily misunderstood or missed, particularly in time-sensitive situations, possibly creating friction in interactions.
Travelers from countries where English is less widely spoken, like China, may require more detailed explanations or additional support, particularly when discussing safety instructions or travel logistics.
In the case of English-speaking travelers, challenges may be more closely linked to differences in expectations, assumptions about local conditions, or communication style rather than language itself.
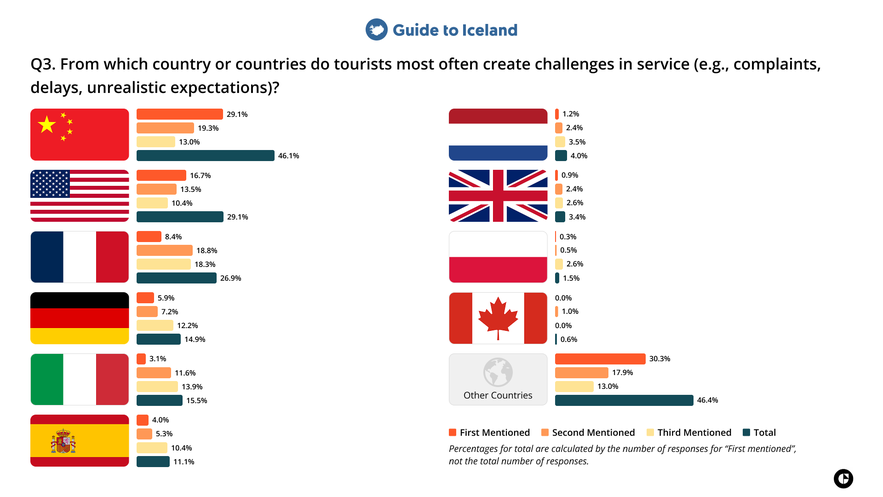
3. From which country or countries do tourists most often create challenges in service?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently selected “Other countries” when asked which travelers most often create challenges in service, indicating that the nationalities they associate with these situations were not among the ten largest source markets listed in the survey.
Among the listed nationalities, travelers from China were most frequently associated with service-related challenges, followed by visitors from the United States and France. The challenges include situations such as complaints, delays, or unrealistic expectations.
Commentary
Service challenges can be influenced by differences in travel culture, expectations around flexibility, and familiarity with how tourism services function in smaller or more remote destinations. Travelers accustomed to highly standardized or fast-paced service environments may find Iceland’s infrastructure, weather-related delays, or operating conditions more restrictive.
Language barriers also affect how smoothly services are delivered, particularly when limitations, delays, or changes need to be explained clearly. When expectations are not fully understood or explanations are harder to communicate, service-related issues are more likely to escalate.
Cultural differences in how dissatisfaction is expressed may also affect which travelers tourism professionals find it challenging to work with.
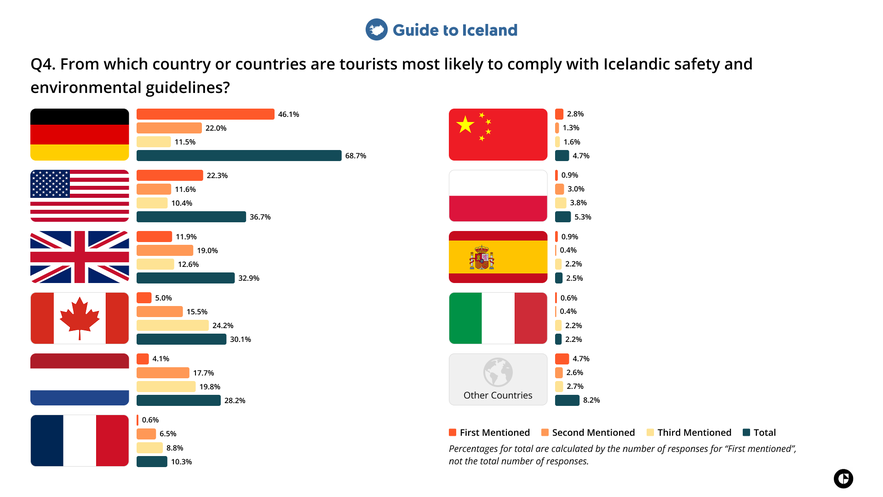
4. From which country or countries are tourists most likely to comply with Icelandic safety and environmental guidelines?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most often associated German travelers with strong compliance with safety and environmental guidelines. Visitors from the United States and the United Kingdom were also frequently mentioned in this category, indicating a higher likelihood of following instructions related to safety, nature protection, and responsible travel.
Commentary
The higher compliance reported for travelers from Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom may reflect broader shared cultural norms around preparation, rule-following, and outdoor responsibility.
Clear communication may also contribute, as travelers who are comfortable communicating in English normally find it easier to understand safety briefings, ask questions, and follow instructions during activities or changing conditions.
In Iceland, compliance with safety guidance is particularly important during activities such as glacier hiking, snowmobiling, ice cave exploration, and guided nature tours, where conditions can change quickly, and risks are not always immediately visible.
Environmental guidelines are equally important, as Iceland’s landscapes are highly fragile, and off-trail walking, driving, or careless behavior can cause long-lasting damage.
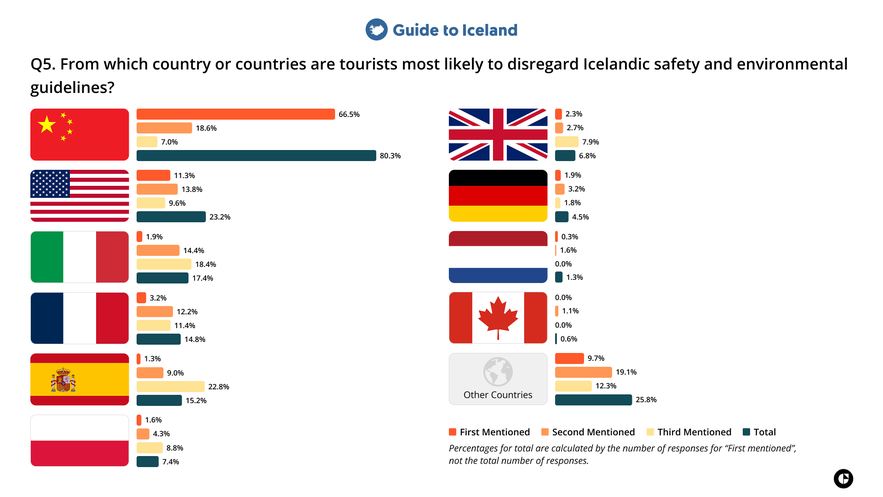
5. From which country or countries are tourists most likely to disregard Icelandic safety and environmental guidelines?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently identified travelers from China as the most likely to disregard safety and environmental guidelines. The second most common response was “Other countries,” indicating that many respondents associate these situations with nationalities outside the ten largest source markets included in the survey.
Among the listed nationalities, travelers from the United States and Italy were also mentioned in relation to situations involving additional safety or environmental guidance, though at notably lower levels than the top-ranked categories.
Commentary
Disregarding safety or environmental guidelines can stem from unfamiliarity with local risks, differences in how rules are communicated or enforced in other destinations, or limited awareness of Iceland’s dangers and fragile natural environment. Travelers who are less accustomed to remote or rapidly changing conditions may underestimate risks and the importance of certain restrictions.
In the survey, groups more frequently associated with disregarding safety and environmental guidelines also appeared more often in the results related to communication difficulties. When information is not communicated efficiently or fully understood, complex or time-sensitive instructions are more likely to be unintentionally overlooked.
Travel mindset also shapes behavior. In “vacation mode,” travelers are often more relaxed and less attentive to risk, especially in unfamiliar environments. This reduces sensitivity to hazards and can result in safety or environmental guidelines being followed less carefully than intended.
The presence of the United States in both compliance-related categories likely reflects its position as Iceland’s largest and most diverse source market, encompassing a wide range of travel styles, experience levels, and behaviors.
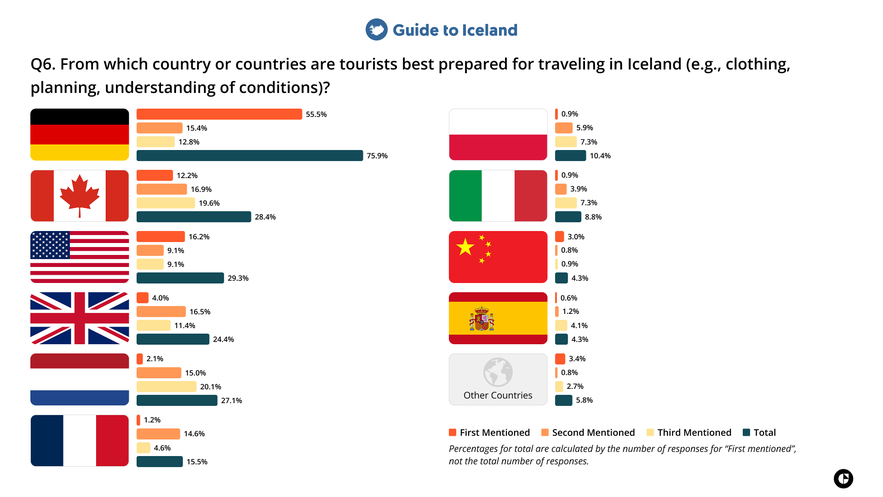
6. From which country or countries are tourists best prepared for traveling in Iceland?
Tourism professionals in Iceland most frequently identified travelers from Germany as the best prepared for traveling in the country. Visitors from Canada and the United States were also commonly mentioned in this category. Preparation in this context includes appropriate clothing, planning, and awareness of Iceland’s weather, terrain, and travel conditions.
Commentary
Differences in preparation are closely linked to differences in travel habits, outdoor experience, and expectations around independent travel. Travelers from countries with strong outdoor cultures or weather conditions similar to Iceland, such as Germany and Canada, tend to arrive better prepared for changing environments and variable conditions.
Preparation is also influenced by access to detailed travel information and familiarity with nature-based destinations. Travelers who research conditions in advance and plan accordingly are more likely to arrive with appropriate clothing, realistic expectations, and awareness of Iceland’s terrain and travel requirements.
The Easiest and "Most Challenging" Tourists According to Tourism Professionals in Iceland
Taken together, the results point less to the “easiest” or “most challenging” tourists in a literal sense and more to consistent patterns in how different visitor groups are experienced on the ground.
Travelers from Germany, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States tend to score higher across multiple categories, particularly in preparation, communication, and compliance with safety and environmental guidelines. These groups are more often associated with smooth day-to-day interactions and fewer situations requiring additional guidance.
By contrast, travelers from China, France, Italy, and Spain appear more frequently in categories related to communication difficulties, service challenges, or situations where additional safety or environmental guidance is needed. In many cases, these patterns align with language barriers, differing travel expectations, or unfamiliarity with Iceland’s conditions rather than intentional behavior.
The United States stands out as a mixed case, appearing prominently in both positive and challenging categories. This likely reflects the size and diversity of the U.S. visitor market, which includes a wide range of travel styles, experience levels, and levels of preparation.
Rather than serving as a judgment, this overview highlights where travel habits and expectations align well with Iceland’s tourism environment, and where targeted improvements can help create safer, smoother, and more positive travel experiences for everyone involved.
Implications and Industry Recommendations

Key opportunities to improve travel experiences include:
-
Providing clear, accessible information in multiple languages, both before arrival and during travel, can help travelers better understand local conditions, safety requirements, and environmental guidelines. Visual materials, signage, and step-by-step instructions can be particularly effective in situations where language barriers exist.
-
Setting accurate expectations early and communicating these clearly throughout the customer journey, from booking and pre-arrival information to on-the-ground guidance, helps travelers understand what to expect in terms of weather, infrastructure, flexibility, and service standards in Iceland and prepare accordingly.
-
Explaining not only what the rules are, but why they matter, especially when it comes to safety and environmental protection, can also encourage better understanding and compliance. When travelers understand the risks involved and the fragility of Iceland’s natural environment, they are more likely to adjust their behavior accordingly.
To summarize, investing in clear, proactive communication benefits everyone involved. Better-informed travelers are more confident, more satisfied, and more likely to have positive experiences, while tourism professionals face fewer misunderstandings and service challenges.
What Travelers Can Do for a Better Experience in Iceland

Key ways travelers can prepare for a trip to Iceland include:
-
Research conditions in advance. Iceland's weather, road conditions, and daylight hours can change quickly. Checking forecasts and road updates regularly helps avoid surprises.
-
Take safety guidance seriously. Weather warnings, signs, and staff instructions are based on real risks. Following them protects both travelers and the natural environment.
-
Prepare for outdoor conditions. Dressing in layers, wearing proper footwear, and planning what to pack and wear with variable weather in mind makes a big difference.
-
Allow flexibility in plans. Weather-related changes and delays are common in Iceland. Booking vacations and tours with experts who can help adjust your plans reduces stress.
-
Ask questions when unsure. Tourism staff are there to help. Clear communication can prevent misunderstandings and improve the overall experience.
By arriving informed and prepared, travelers are better equipped to enjoy Iceland’s landscapes responsibly while helping preserve them for future visitors.
Conclusion

For the tourism industry, investing in communication is not only a matter of safety and sustainability, but also of long-term success. Clear guidance, transparent expectations, and accessible information in several languages contribute to higher satisfaction, stronger reviews, positive word of mouth, and more sustainable tourism growth.
By supporting travelers with the right information at the right time, Iceland’s tourism sector can help ensure safer experiences, better interactions, more memorable journeys, and sustainable long-term growth for the industry.