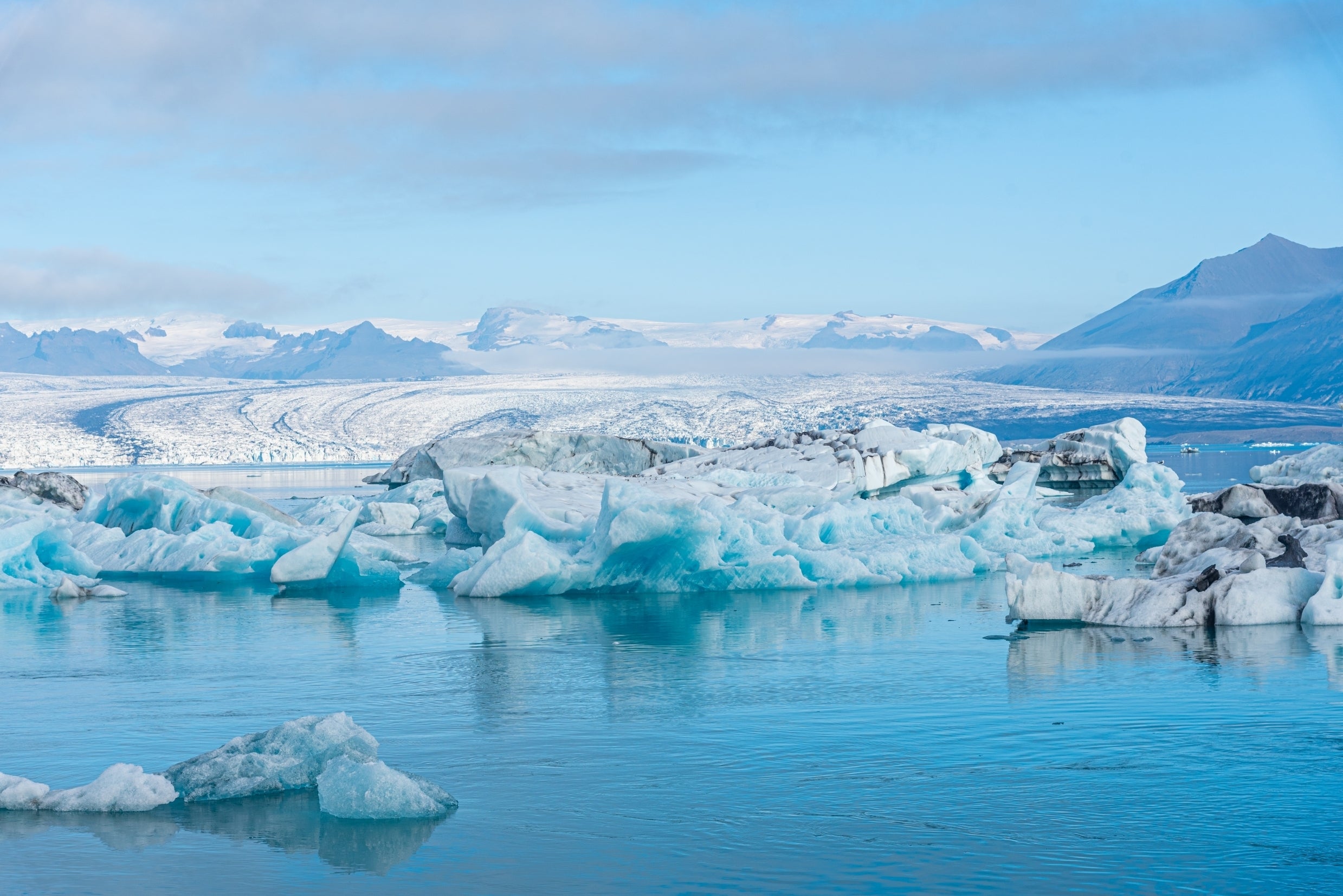
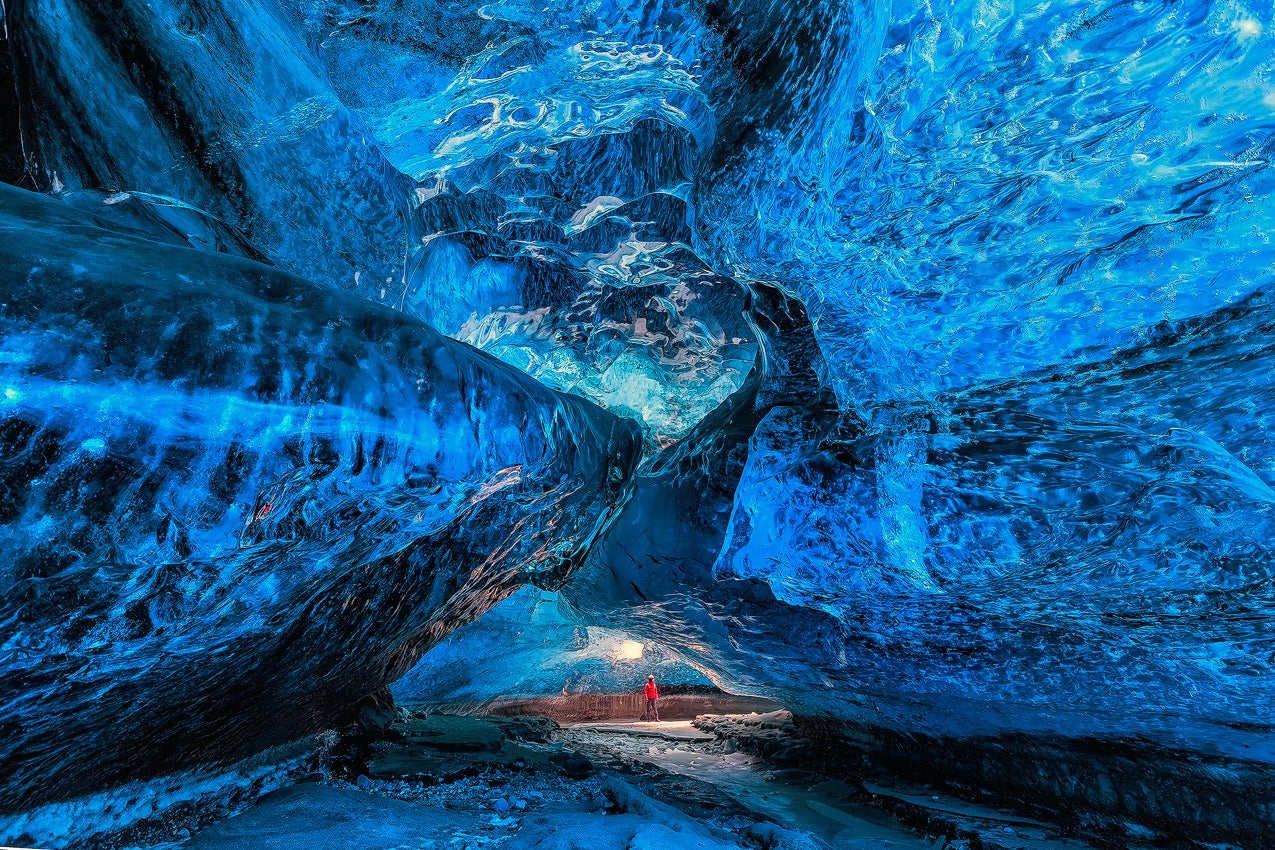
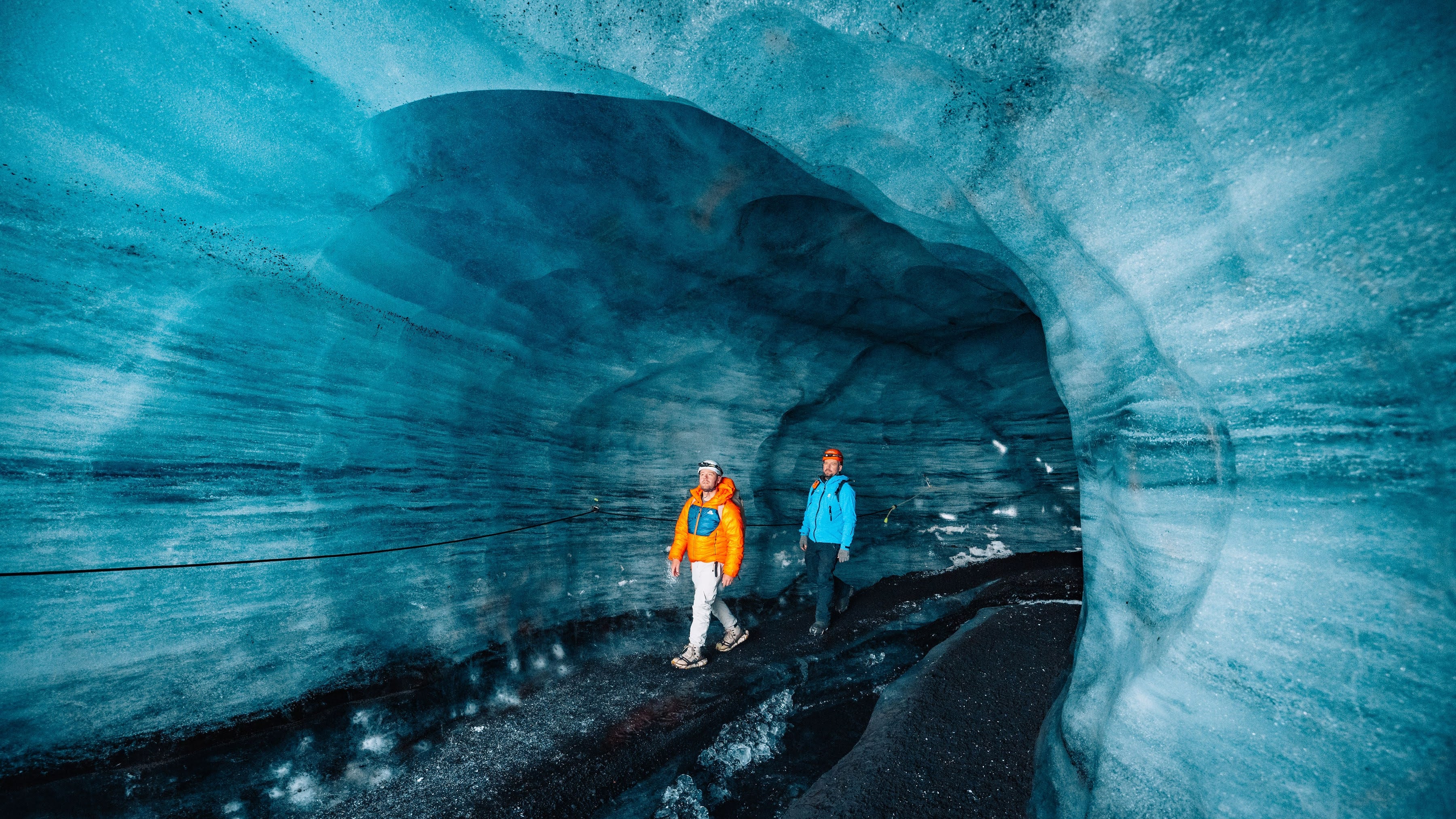
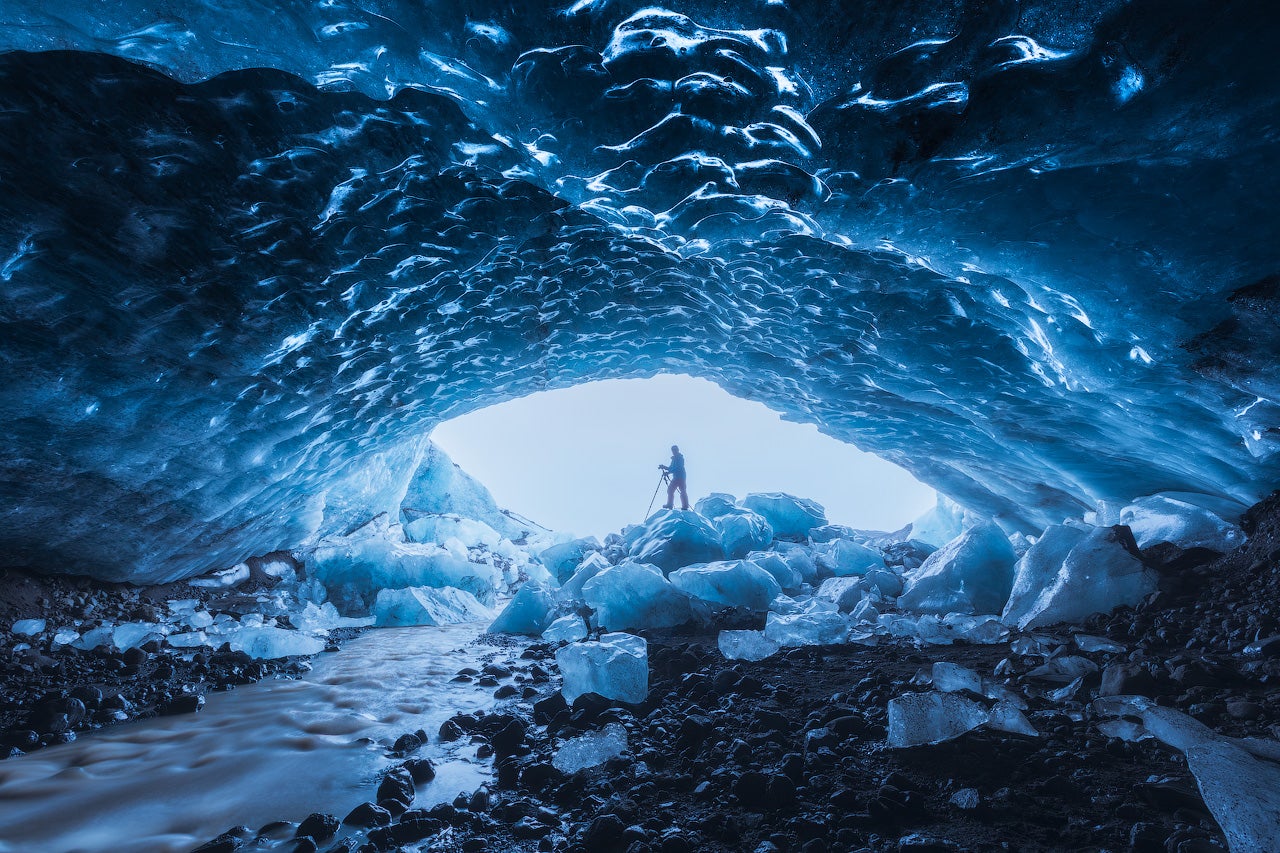
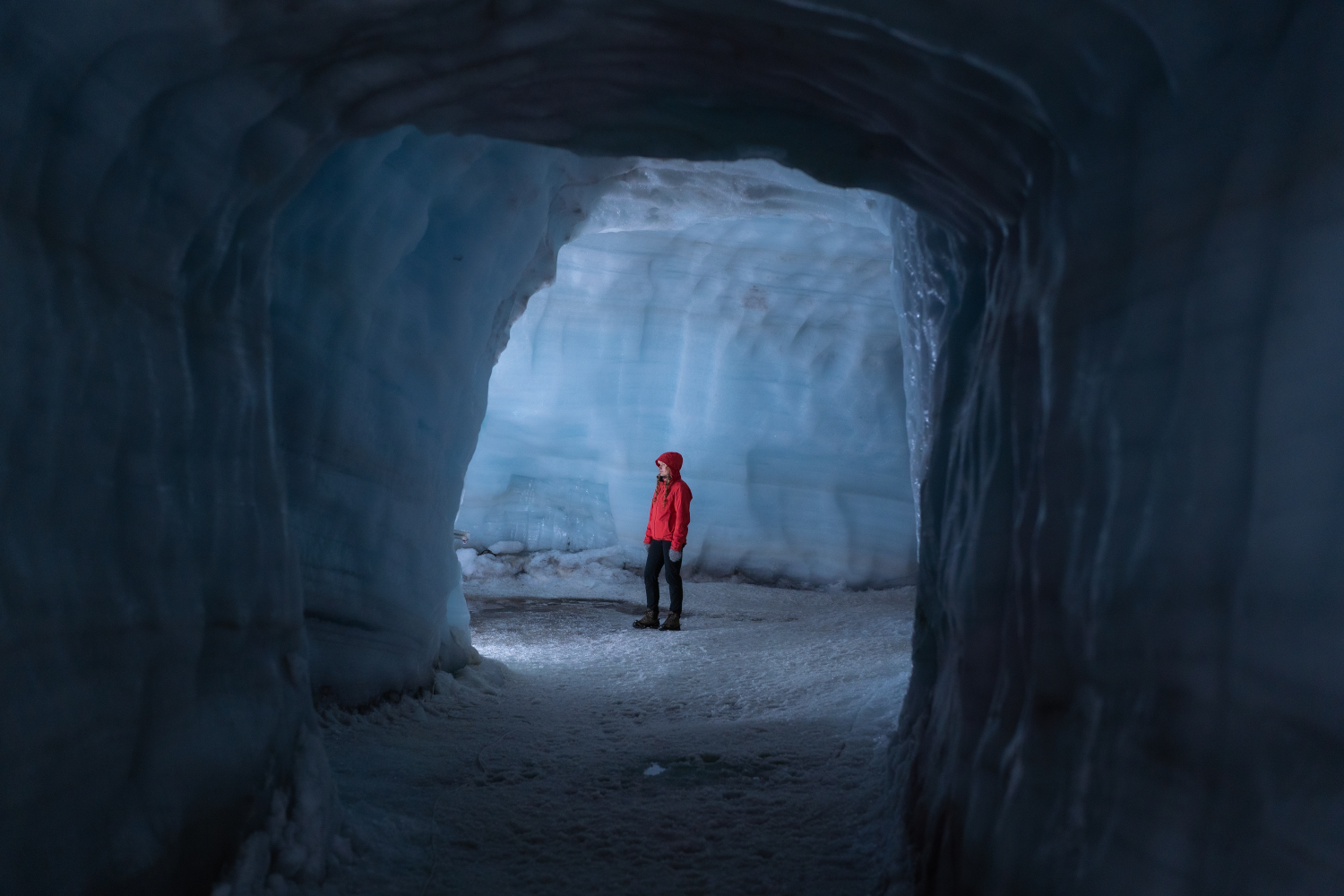
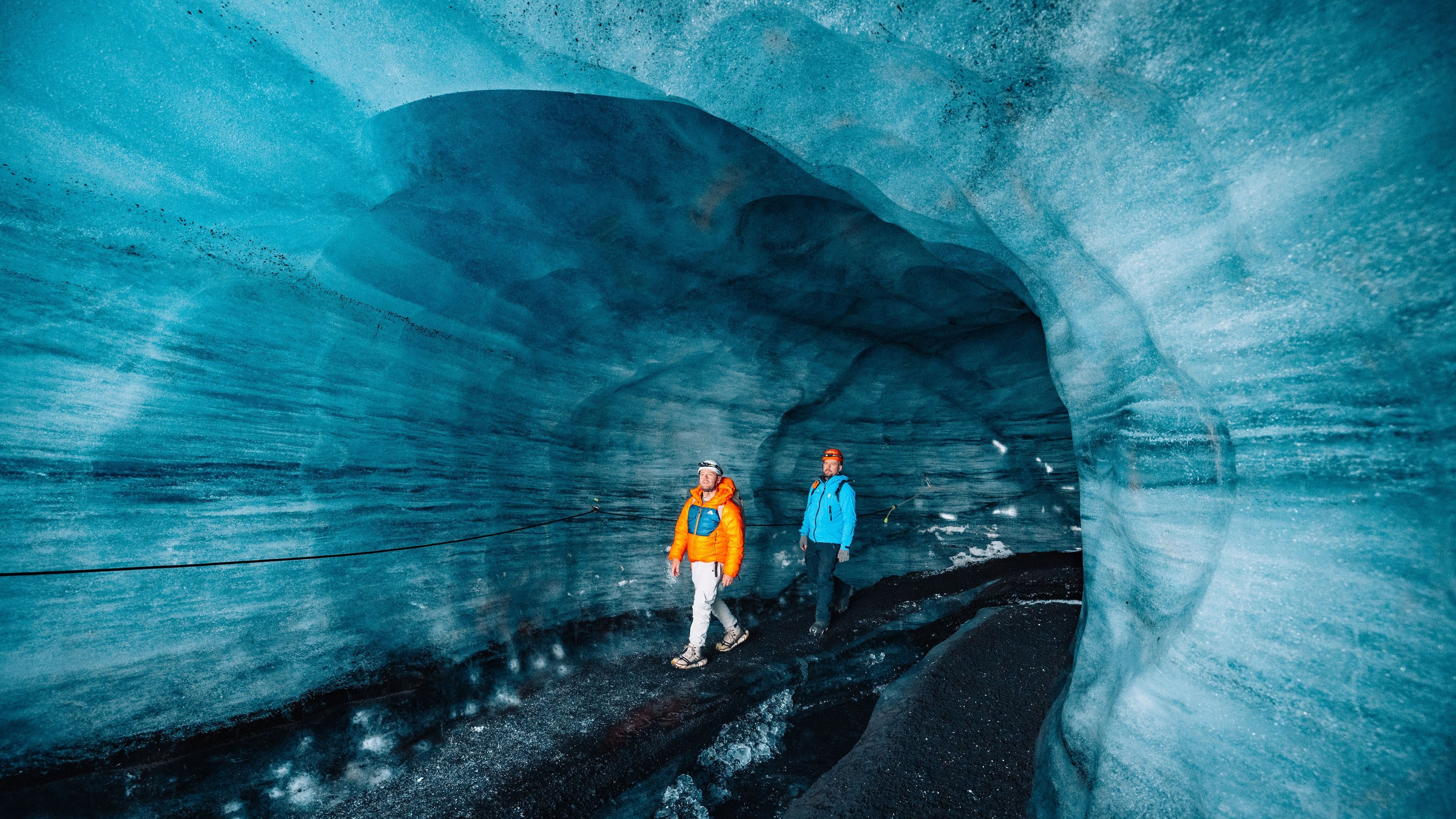
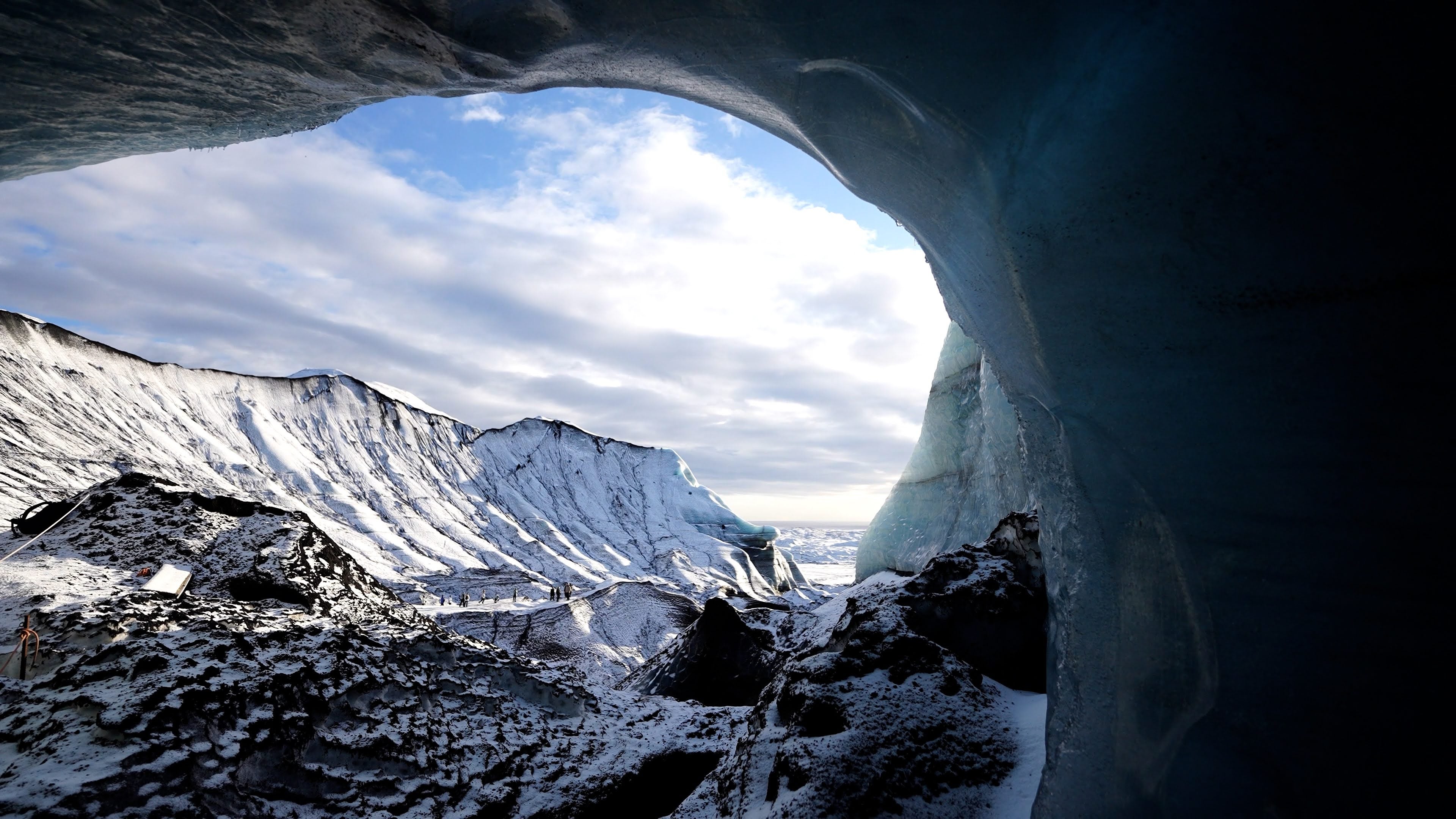
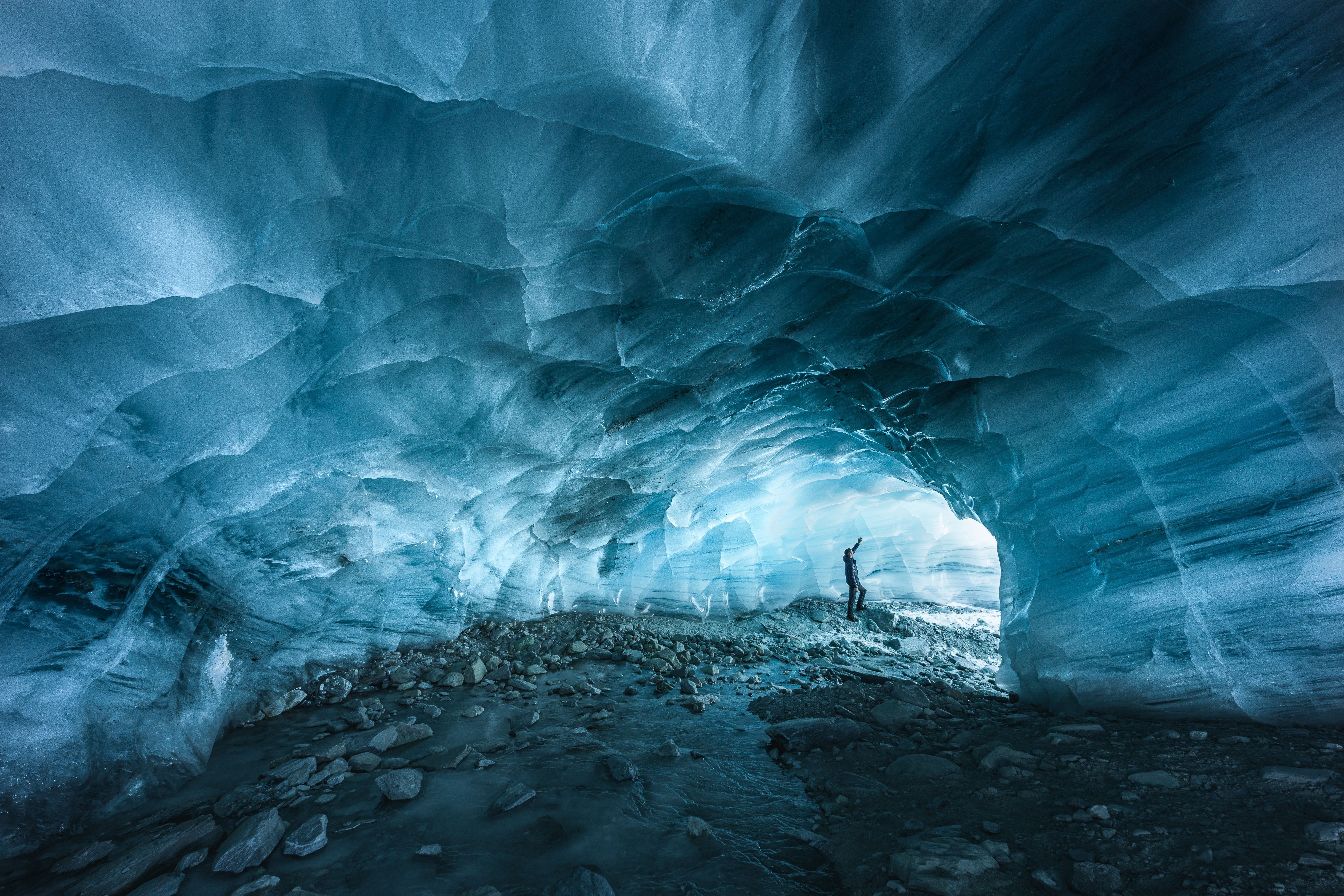
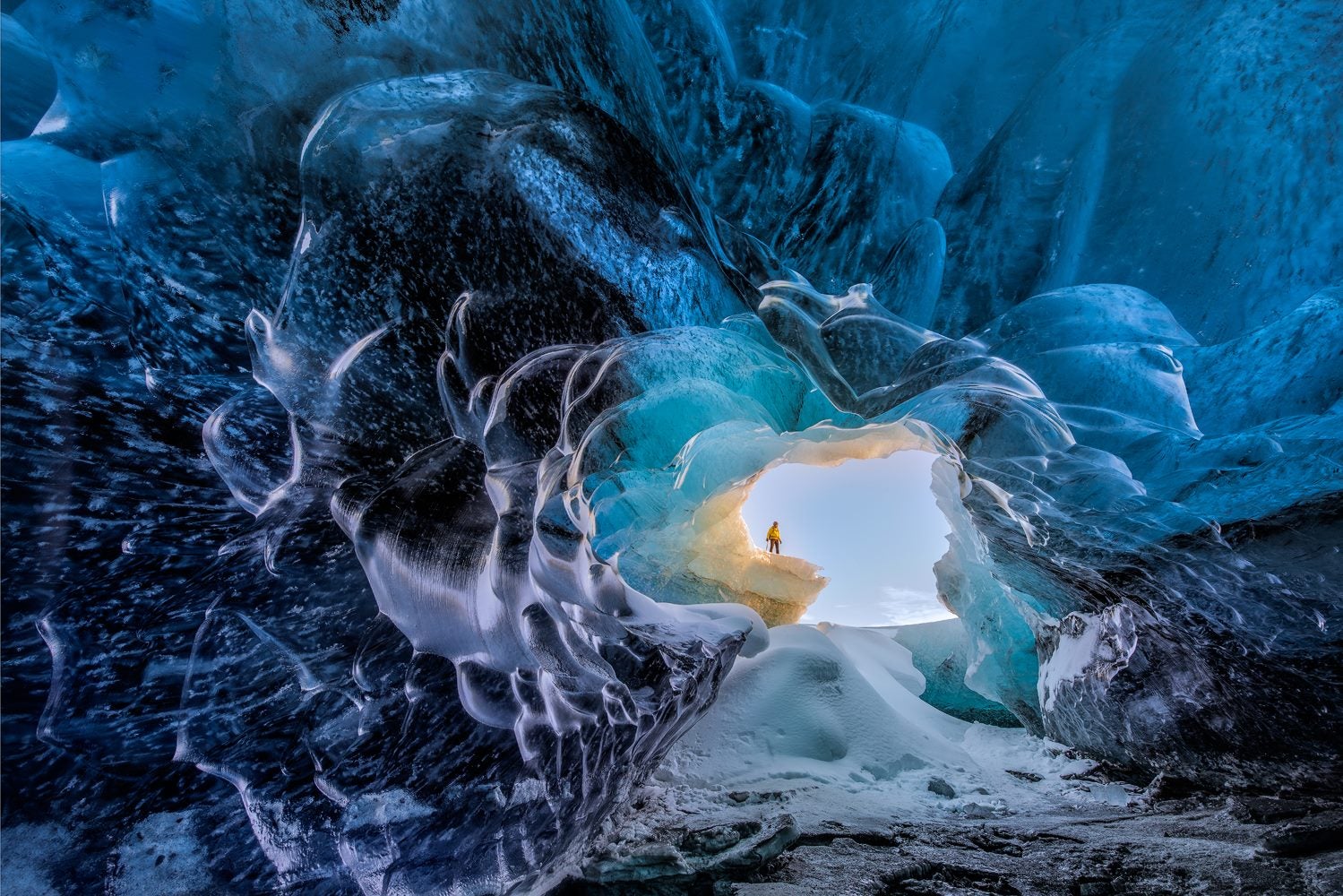
Ice cave tours in Iceland offer a rare opportunity to enter a glacier and see stunning natural formations of vivid blue, white, and crystal-clear ice. Each tour begins with a scenic journey to one of Iceland’s major glaciers, followed by a guided walk or a ride in a specially equipped vehicle across the ice to reach the cave’s entrance.
Inside the cave, visitors are surrounded by shimmering blue walls, layered ice formations, and frozen air bubbles that catch the light, creating an unforgettable visual experience.
The Best Time to Visit Ice Caves in Iceland
The best time to visit ice caves in Iceland is during winter, from November to March, when the ice is most stable and safe to explore. Natural caves, like those in the Vatnajokull glacier, form brilliant blue structures during this season and can be visited with expert guides.
Some caves, such as the Katla Ice Cave and Langjokull Ice Tunnel, are accessible year-round, but winter offers the most dramatic and authentic ice cave experiences, revealing Iceland’s glacial landscapes at their most striking.
Top 5 Ice Cave Tours in Iceland
To help you choose the best ice cave for your adventure, here is a list of the current top 5 ice cave tours in Iceland.
1. Crystal Ice Cave Tour from the Glacier Lagoon
Within Vatnajokull, the largest glacier in Europe, you can embark on the breathtaking Crystal Ice Cave Tour. This winter, in 2024/2025, visitors can explore the stunning ice cave with vivid blue hues and crystal-clear walls often compared to a sparkling blue diamond.
This tour takes you to the most spectacular Crystal Ice Cave of the season, ensuring a safe and unforgettable experience. The cave, a natural marvel, is only accessible during the winter months, showcasing Iceland's stunning and pristine ice formations. Discover winter's best ice cave on this top-rated tour departing from Jokulsarlon Glacier Lagoon.
Where is Crystal Ice Cave?
The Jokulsarlon Glacier Lagoon in South Iceland, with its floating icebergs, is worth a visit on its own. It's also a meeting point for the best ice cave tours in Iceland, which will take you to the crystal ice caves of Vatnajokull Glacier.
How To Get to Crystal Ice Cave
The tour departs from the Jokulsarlon Glacier Lagoon in southeast Iceland, located approximately 5 hours (380 km) from Reykjavik by car. To get there:
-
Take the Ring Road (Route 1) east from Reykjavik.
-
Follow the road signs to Jokulsarlon glacier lagoon near Vatnajokull National Park.
-
Parking is available at the lagoon, and tour operators will meet you there.
2. Katla Ice Cave Tour from Vik
Located near the town of Vik in South Iceland, over the active Katla Volcano and beneath Myrdalsjokull Glacier, the Katla Ice Cave combines black volcanic ash with glacial ice, creating striking contrasts of blue and black. Available to visit year-round, the Katla Ice Cave tour provides a unique twist for those interested in Iceland’s volcanic and glacial landscape.
Where is Katla Ice Cave?
Vik is a charming village on the South Coast of Iceland is well known for its iconic Reynisfjara Black Sand Beach and the mysterious Reynisdrangar Sea Stacks, which can be seen from its shore. It's also the meeting point for visiting the breathtaking ice cave in Katla, making it an ideal place to visit for more than one reason.
How To Get to Katla Ice Cave
The tour begins near Vik, a town in South Iceland about 2.5 hours (180 km) from Reykjavik by car. To reach Vik:
-
Drive east on the Ring Road (Route 1) from Reykjavik.
-
Pass through Hvolsvollur and continue until you reach Vik.
-
Most tours have a meeting point near Vik or provide transportation from the town.
3. Skaftafell Ice Cave in Southeast Iceland
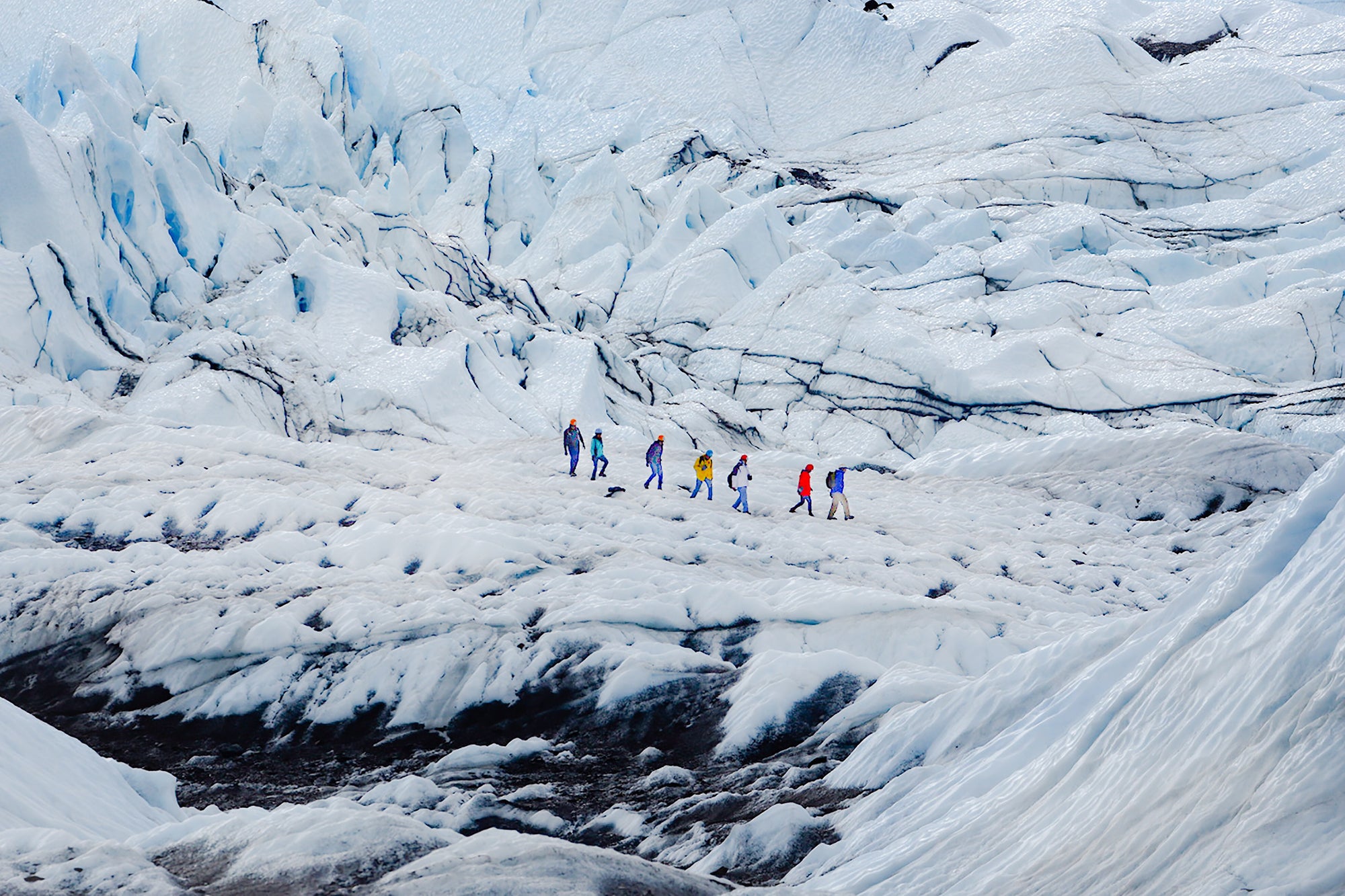
Located within Vatnajokull National Park, the Skaftafell Nature Reserve is perfect for visitors seeking various nature experiences. The Skaftafell Ice Cave is located in the Falljokull Glacier and is known for its delicate textures and vibrant colors. Visiting this ice cave is only possible during winter and is often paired with other activities in the park, like hiking and waterfall exploration. This glacier is ideal for those looking for a more challenging ice cave tour.
Where is Skaftafell Ice Cave?
Skaftafell Nature Reserve is a protected region in Iceland, famous for its amazing hiking trails and the striking Svartifoss Waterfall known for its basalt columns. It's also where the adventurous glacier hike toward the beautiful ice cave in Falljokull Glacier starts.
How To Get to Skaftafell Ice Cave
Skaftafell is located within Vatnajokull National Park, about 4 hours (300 km) east of Reykjavik. To reach Skaftafell:
-
Take the Ring Road (Route 1) east from Reykjavik.
-
Follow signs to the Skaftafell Visitor Center, where many tours begin.
-
Ensure you arrive early to meet your guide and receive equipment for the glacier hike.
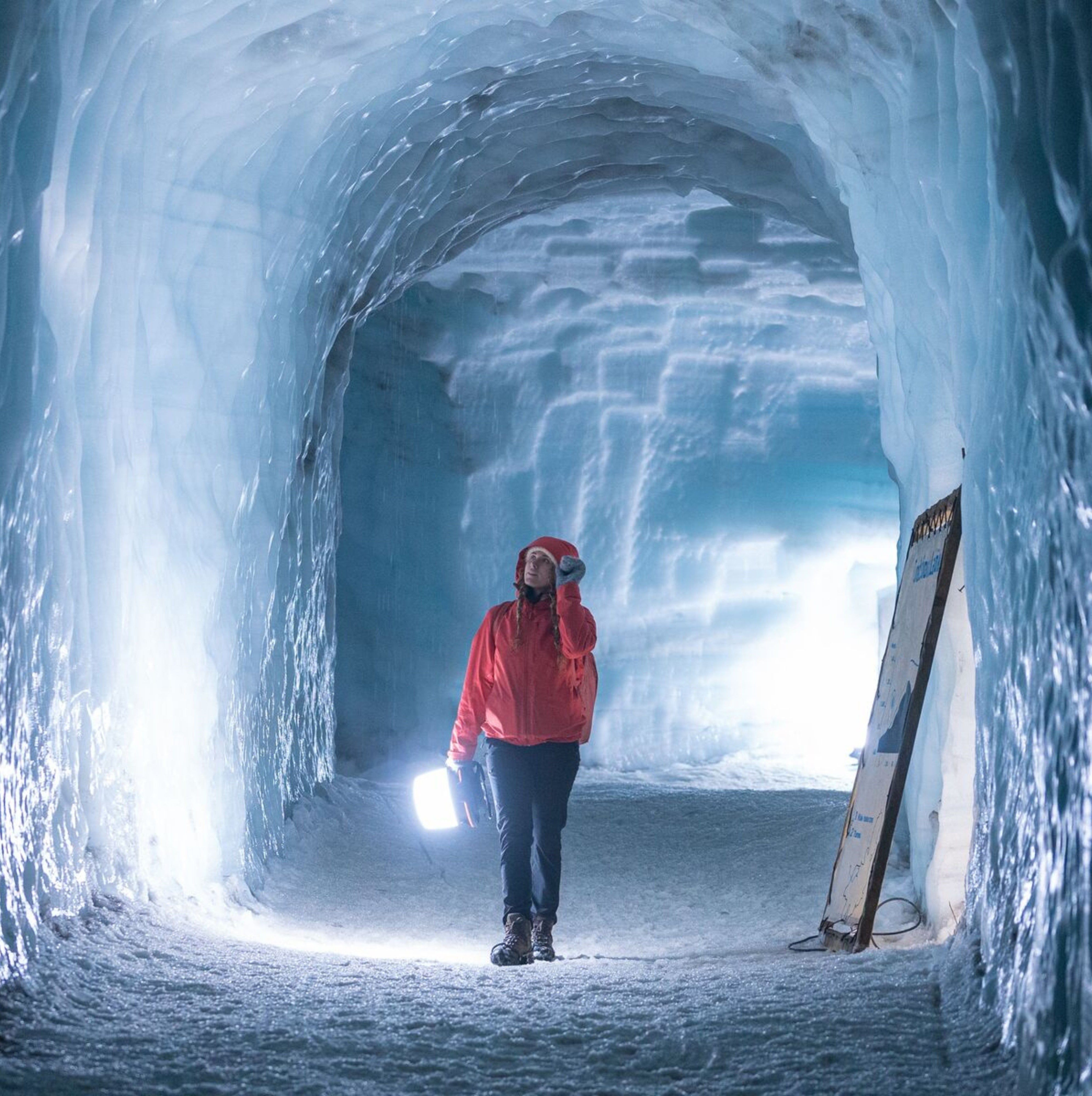
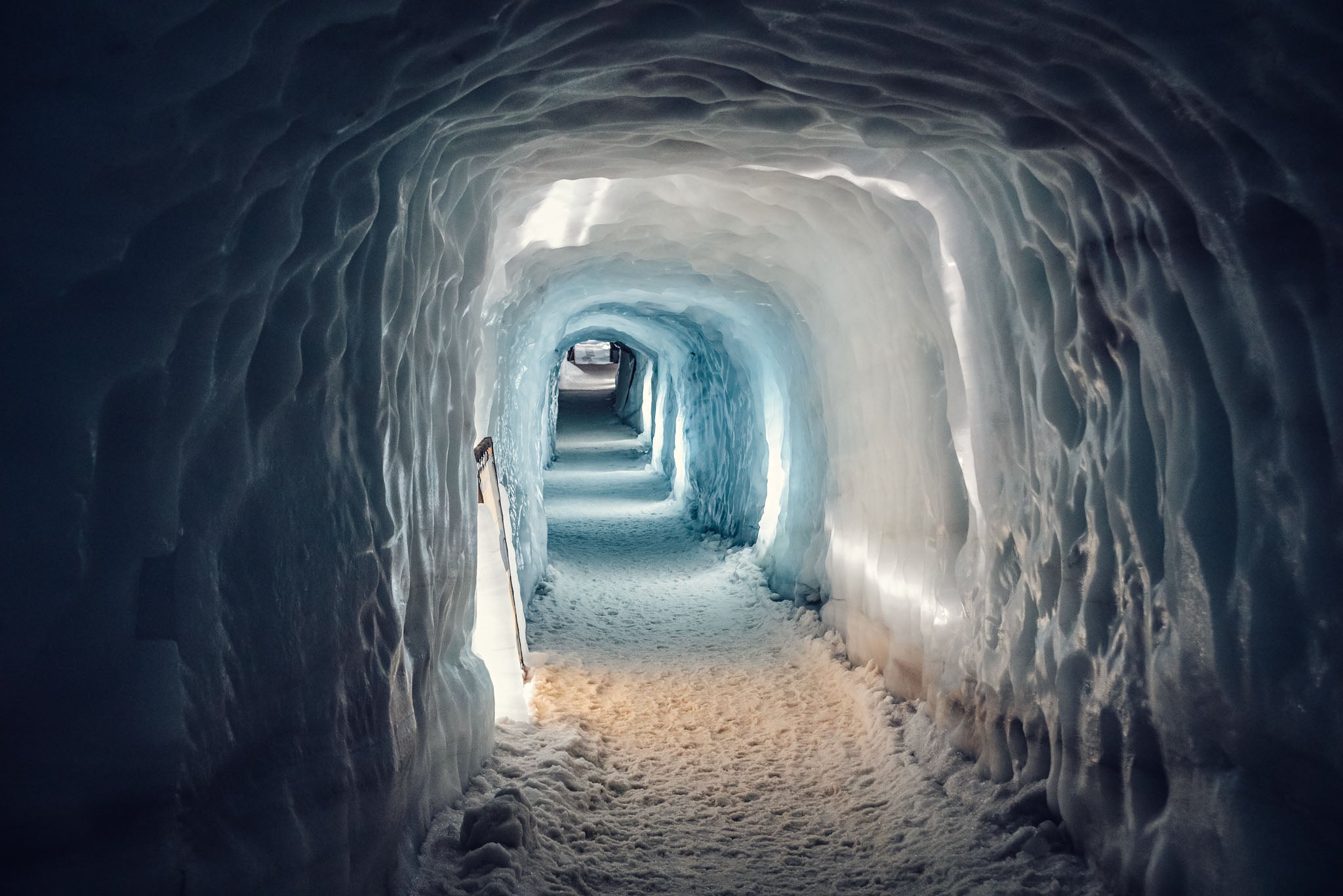
4. Langjokull Glacier Cave tunnel
Located in West Iceland, near the Golden Circle, the Langjokull Ice Cave is a captivating man-made ice tunnel that provides year-round access to the heart of the glacier. This unique cave takes visitors deep within Langjokull, where layers of ancient ice reveal the glacier’s rich history. The well-known Into the Glacier Tour is the ideal option for families with children and for those looking to experience Iceland’s icy wonders, even outside the winter season.
Where is Langjokull Ice Cave?
The Langjokull Base Camp is located on the edge of the magnificent Langjokull glacier. Also known as "Klaki," it's where adventurous travelers gather before embarking on a journey into the glacier ice tunnel of Langjokull, which can be visited year-round. Keep in mind that to get there, you need to drive an F-road, so make sure you have a 4x4 rental.
How To Get to Langjokull Ice Cave
Tours to the Langjokull ice cave often start near Husafell in West Iceland, about 2 hours (130 km) from Reykjavik. To get to Husafell:
-
Drive north on Route 1 from Reykjavik, then take Route 50 toward Borgarnes.
-
From Borgarnes, take Route 518 to Husafell.
-
Tour operators will usually arrange specialized glacier vehicles for the final leg to Langjokull.
5. Lofthellir Ice Cave in North Iceland
Located in North Iceland, the impressive Lofthellir Ice Cave is a fascinating volcanic cave that features incredible ice formations. Known for its ancient stalagmites and unique lava tube structure, Lofthellir is accessible year-round and offers a unique experience different from glacier-based ice caves. Join this Lofthellir ice cave tour from Lake Myvatn and experience it in all its glory.
Where is Lofthellir Ice Cave?
Lake Myvatn in North Iceland is known for its pseudocraters, rock formations, and geothermal activity. Lake Myvatn is also the meeting point for those wanting to visit the stunning Lofthellir Ice Cave, the only ice cave that you can visit in Iceland's northern region.
How To Get to Lofthellir Ice Cave
The Lofthellir Ice Cave tour typically departs from Lake Myvatn, located in North Iceland, about 6 hours (475 km) from Reykjavik by car. To get to Lake Myvatn:
-
Drive north on Route 1 from Reykjavik, passing through Akureyri.
-
Follow Route 1 east to Lake Myvatn.
-
Many tours start from the lake area, with transport provided to the cave itself.
Each of these destinations offers a distinct experience of Iceland's natural beauty, revealing breathtaking views of the country’s ice formations and glacial landscapes. An ice cave tour is a one-of-a-kind opportunity to witness Iceland’s glacial beauty in its purest form.
Ice Cave Tours with Pickup from Reykjavik
Visiting an ice cave while staying in Reykjavik is simple and easy. There are multiple ice cave tours available that offer pickups from Reykjavik, allowing people to be transported from the capital to the ice cave with no hassle. Here are our favorite ice cave tours with pickup from Reykjavik:
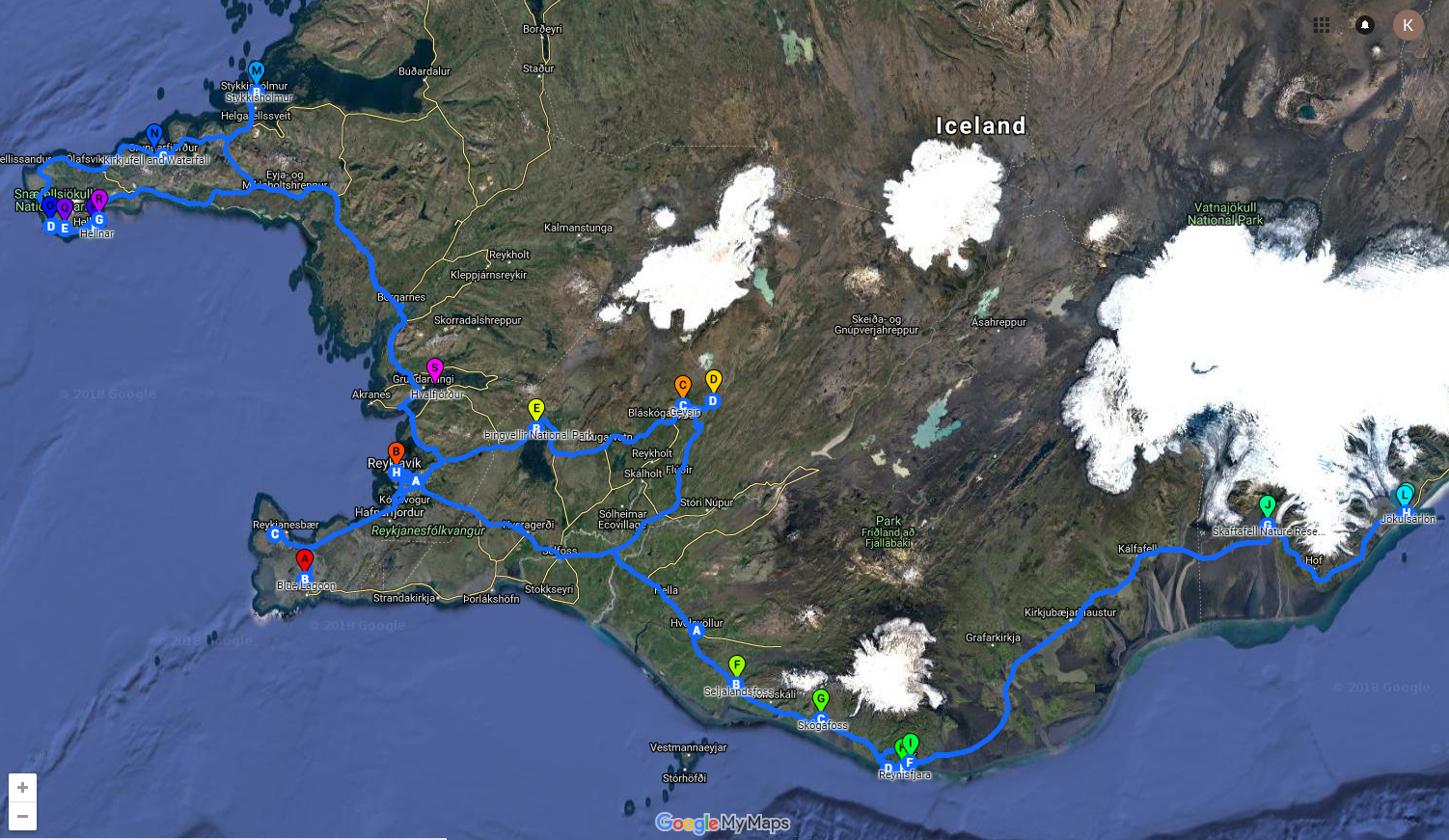
Multi-Day Ice Cave Tours Starting from Reykjavik
For those wanting to experience the magic of ice caves while traveling to other destinations around Iceland on a multi-day tour with a pre-planned itinerary, here are some of the best travel packages that take you to ice caves in Iceland.
Ice cave tours are available for different skill levels and include all the necessary equipment and guidance from professionals trained in glacier safety, ensuring a comfortable, safe, and enriching journey for everyone.
It’s important to note that weather conditions in Iceland ultimately determine whether an ice cave tour will go ahead. Many tour operators offer free rescheduling to another day in case of cancellations, but safety always comes first. Participants should wear warm, waterproof layers and sturdy boots, as conditions in and around the caves can be cold and slippery.